
Section 514 identification and notices in the Amendment No. 2 Draft for Public Comment
Table 51 – Identification of conductors
Table 51 sets out the specific designation system of colour or alphanumeric code for identification conductors, and is referenced by Regulations 514.4.4, 514.4.6 and 514.5.3. There are effectively three changes to this Table:
- the use of Pink for the identification of a conductor whose sole purpose is a functional earth, along with the alphanumeric designation FE, was implemented by Corrigendum 2018, to align with the harmonized standard BS EN 60445:2017 Basic and safety principles for man-machine interface, marking and identification. Identification of equipment terminals, conductor terminations and conductors.
- a proposed change to the colours used to identify + and – conductors in DC systems. M conductors in DC systems, which are current-carrying conductors earthed at one point in the system, are to remain Blue. This change, also aligning with BS EN 60445:2017, results from the need to be able to distinguish the live conductors of DC systems from those of AC systems, due to the increase in the use of low voltage (LV) and extra-low voltage (ELV) DC in modern installations.
- the presentation of colours in the Table with a two-letter code in brackets after the colour. The two-letter code for identification of conductors has been in place since 1993 in BS 7645 (implementing CENELEC Harmonization Document HD 457 S1:1985), in addition to being used in BS EN 60445:2017.
These proposed changes are also reflected in proposed updates to Appendix 7. In addition, the informative Appendix 7 Harmonized cable core colours includes a new item 8: Colour codes for diagrams and specifications, which summarizes (in Table 7F) the BS 7645 colour codes, and recommends that they are used, where required, to identify conductors in operation and maintenance information, such as wiring diagrams and termination schedules.
Proposed new Regulation 514.9.2
As BS 7671 is now published in digital as well as print format, it is no longer feasible to try to identify the minimum size of text on notices with words such as “not smaller than those illustrated here”. In addition, there are harmonized standards for instructions, technical documentation and safety signs, which apply independently of BS 7671.
The key considerations for implementing new requirements for labelling were:
- the need for the majority of existing labels to comply with the new requirements.
- the option for flexibility in the sizing of labels, as the standards for safety signs and instruction notices permit the use of smaller labels on smaller surfaces. For example, an instruction notice for six-monthly testing of a residual current device (RCD) installed in a 2-module enclosure could now have a label with 7 pt (2.5 mm height) text if printed in black on a white background (see Figure 1), if it were applied on a 2-module enclosure having a surface area of less than 10 cm2.
Figure 1 Examples of the label required by proposed Regulation 514.12.2
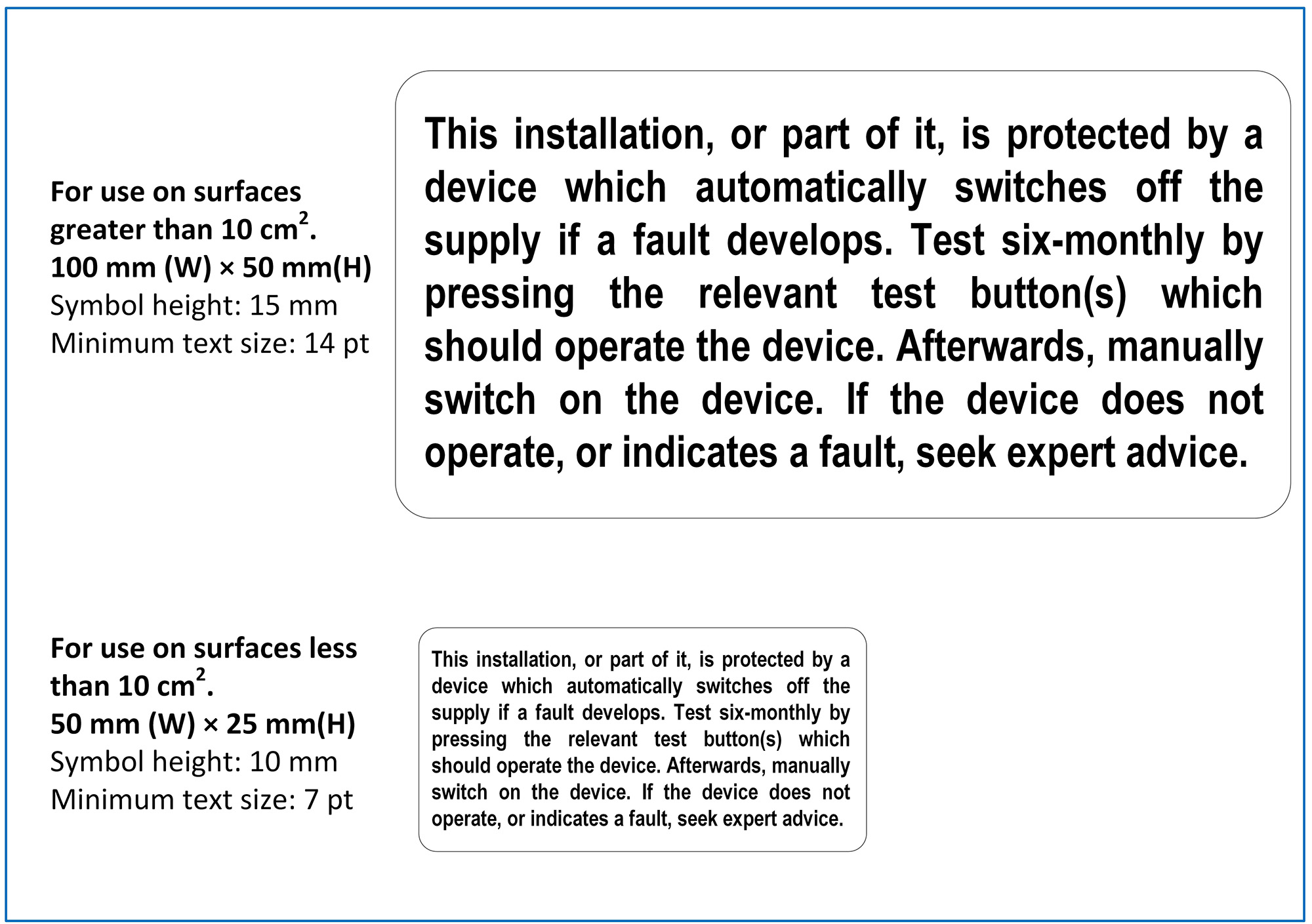
To simplify the specification of signs and notices in BS 7671, Regulation 514.9.2 is proposed. This proposed Regulation states:

The key elements of the requirement are:
- that all user instructions, notices and operating and maintenance information comply with the relevant standards for technical documentation (BS EN 61082-1, plus BS EN 81346-1 for certain industrial systems) and user instructions (BS EN IEC/IEEE 82079-1) and
- that all warning notices and relevant safety signs comply with the relevant standards for safety signage, which, in any case, would be required to comply with the Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals Regulations) 1996:
- BS EN ISO 3864 covers the basic design of safety signs
- BS EN ISO 7010 is the standard that documents registered safety signs, for example, the electricity hazard (lightning bolt in a triangle) sign and
- BS EN IEC/IEEE 82079-1 specifies the size of symbols and text used in safety signs.
All signs and notices in the Draft for Public Comment are classified as either:
- a warning notice, which is intended, for example, as a safety warning or
- an instruction notice, intended to provide information or instructions for users of the installation.
In order to assist installers and those carrying out initial and periodic verification, guidance is provided in the proposed Appendix 11 on labelling requirements to BS EN IEC/IEEE 82079-1.
Changes to Regulations specifying signs and notices
Where necessary, Regulations in BS 7671 specifying signs and notices have had their terminology modified to align with their classification as either warning notices or instruction notices.
It is also recognized that, for domestic (household) premises, certain instruction notices providing general information can be provided with other documentation, accompanying the Electrical Installation Certificate (EIC), where it is not practicable or desirable to fix the notice in the premise.
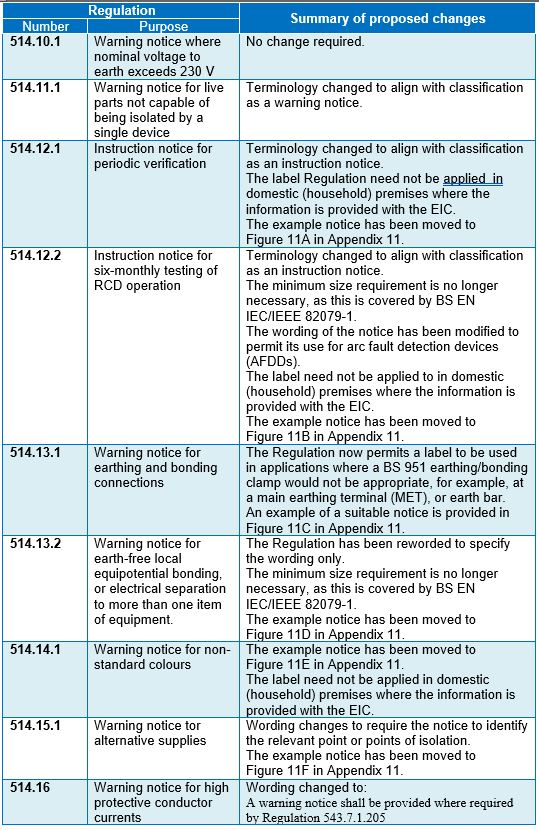
Table 1 summarizes the proposed changes to the Regulations specifying signs and notices in BS 7671.
Table 1 Proposed changes to the Regulations for signs and notices in BS 7671
Appendix 11 (informative)
A new Appendix 11 is included in the Draft for Public Comment, containing guidance on the requirements for labelling, aimed at those carrying out erection, initial verification and periodic verification.
The Appendix advises on the minimum requirements for text and symbol size, summarized in Table 2 below. In addition, it advises the use of an easy-to-read sans serif font, giving examples of Arial, Calibri, Helvetica and Verdana.
Examples of labels in these sizes are shown in Figures 1, 2 and 3.
Table 2 Minimum label text and symbol sizes to BS 7671
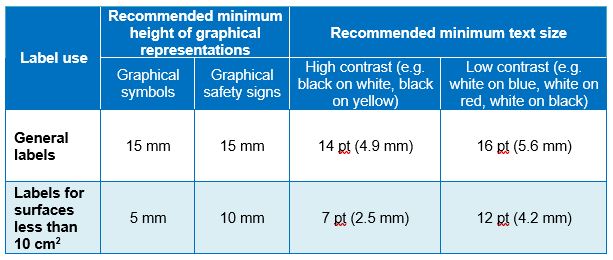
Appendix 11 also contains illustrated examples of notices required by Regulations 514.11.1, 514.12.2, 514.13.1, 514.13.2, 514.14.1 and 514.15.1. Where relevant, examples are shown for general labels and those for surfaces of less than 10 cm2.
The Appendix also recognizes that some of the signs and notices may, in modern installations, be provided on electronic displays, where there are additional standards for legibility.
Figure 2 Examples of the label required by proposed Regulation 514.13.1, when the label is not part of an earthing/bonding clamp to BS 951
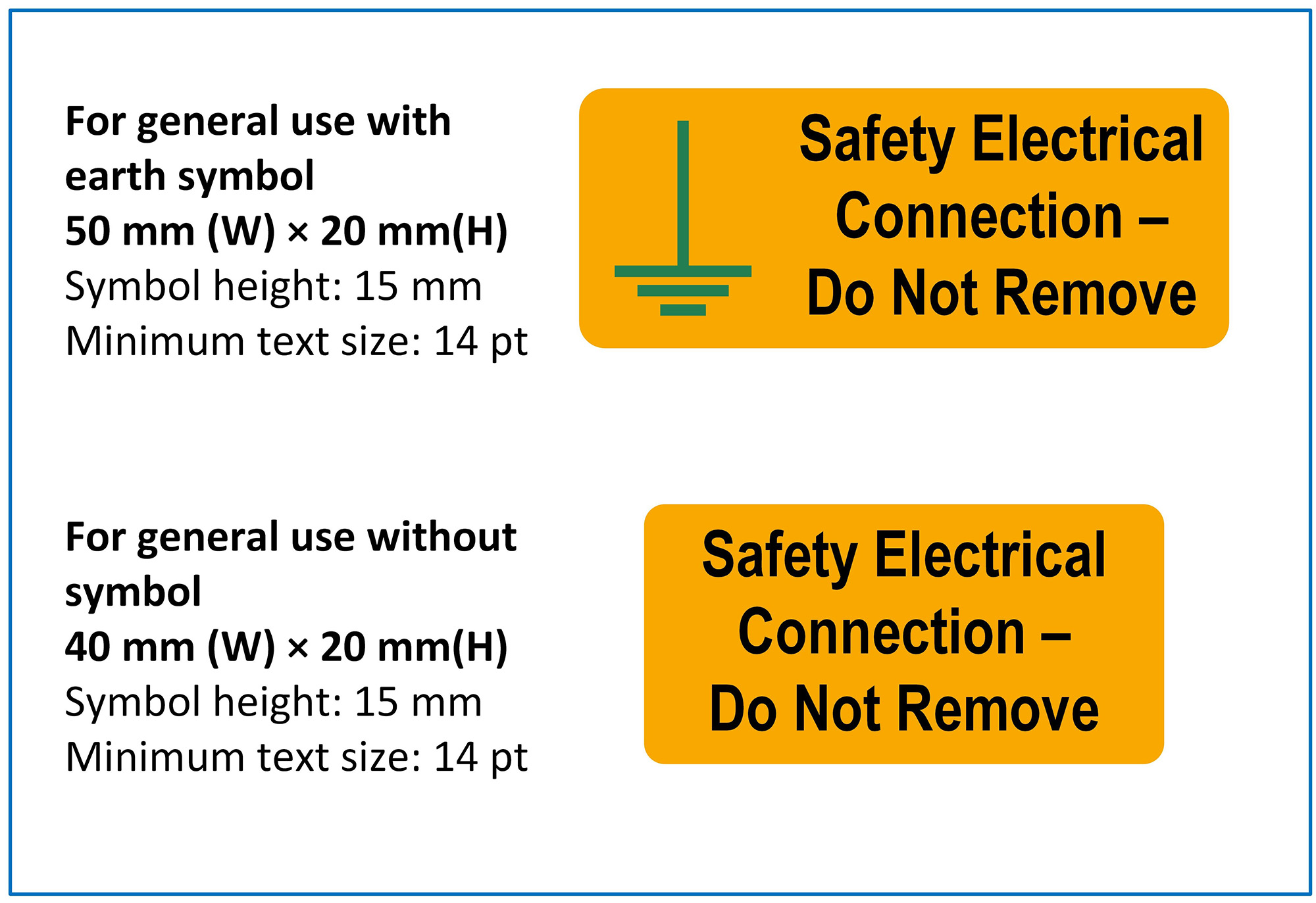
Figure 3 Examples of the label required by Regulation 514.14.1

References
- BS 951:2009 Electrical earthing. Clamps for earthing and bonding. Specification
- BS 7645:1993, IEC 60757:1983 Code for designation of colours
- BS EN IEC/IEEE 82079-1:2020 Preparation of information for use (instructions for use) of products. Principles and general requirements
- BS EN 60445:2017 Basic and safety principles for man-machine interface, marking and identification. Identification of equipment terminals, conductor terminations and conductors
- BS EN 61082-1:2015 Preparation of documents used in electrotechnology. Rules
- BS EN 81346-1:2009 Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial product. Structuring principles and reference designations. Basic rules
- BS ISO 3864-1:2011 Graphical symbols. Safety colours and safety signs. Design principles for safety signs and safety markings
- BS EN ISO 7010:2020 Graphical symbols. Safety colours and safety signs. Registered safety signs
- Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals Regulations) 1996
